It doesn't matter if you are looking to invest your money, or increase your return on your investment, it is important to know the differences between preferred and common stock. Preferred stocks offer smaller dividend yields but do not offer as much growth potential. Common stock dividends can be significantly higher than their preferred counterparts in the long-term. But preferred stocks are a quick way to increase your dividend income.
Differences between preferred stock (common stock)
The common stock and preferred stocks are both forms of ownership in companies. They are both forms of ownership in companies and allow investors the opportunity to profit from the company's successes. We will examine the differences between each, and why one may be better for some investors than the other. Here are some of the advantages of each type of stock. Before you buy any type of stock, it is important to know the differences. This information could be very useful when you are looking into financing options for your company.
A preferred stock has the advantage of paying dividends. Common stockholders are not entitled to arrears in dividend payments. But preferred stockholders are entitled to their voting rights if a company doesn't pay a dividend in three years. Both stocks offer their benefits, but it is important that you understand your investment goals before choosing one. The following information is intended to provide general guidance. It is not intended as tax advice or as an attempt to avoid federal penalties. Please seek independent tax advice before making any investment decision.

Dividends in preferred stock
The dividend rate is what determines the difference in common stock and preferred stocks. The preferred shares pay fixed dividends at a rate determined by the stock's par value at the time of offering. Common stock dividends however are variable and may be paid at any time by the board. The dividend amount remains constant, but the market yield varies with the stock's price.
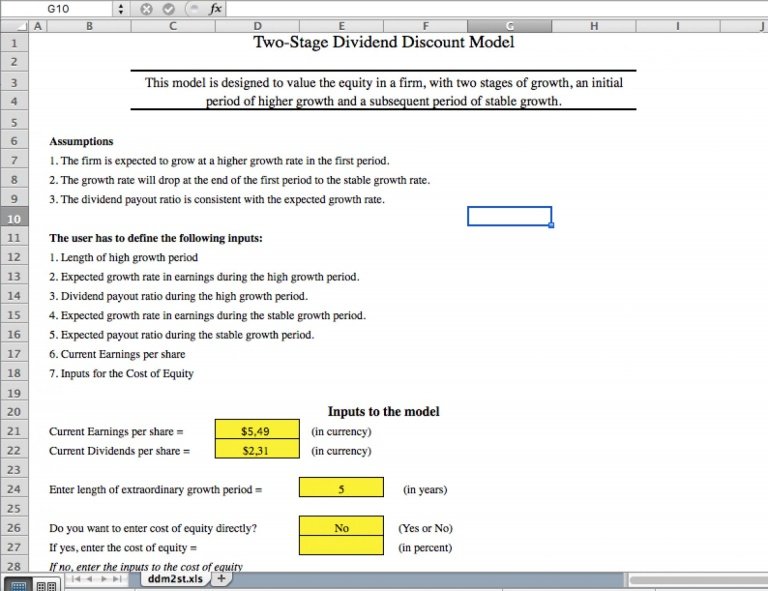
The dividend rate of common stocks tends to be more favorable than the rate of preferred stocks. Dividends are more predictable and stable in preferred stock, but their growth potential is limited. The market interest rate determines the price of common stock, while that of preferred stock is determined by its par value. Preferred stock dividends pay a lower tax rate than bond interests, which gives the preferred stock an edge over common stock. But, this advantage also has its downsides.
Convertible preferred Stock
It is important to understand the differences between convertible preferred stocks and common stock when you are looking to purchase shares of a startup. Understanding the differences between these two types of shares will be easier if you know the conversion ratio. The conversion rate is the ratio of the par amount to the current common stock price to make the preferred stock worthwhile to convert. Ideally, the conversion ratio should be higher than five.
Convertible preferred stock has certain advantages over common stock. It can also be traded on the secondary marketplace, and its value is often more stable. Contrary to common stock, convertible preferred stock's resale value is linked to the conversion premiums. This can lead to preferred stock values fluctuating depending on whether the conversion premium is paid. Convertible preferred stocks may not pay a dividend since the value of the preferred shares is tied directly to the par value.
Non-participating preference Stock
If you've ever invested in the preferred stock or common stock of a company, you might wonder if they are equal. The difference between the two is that the non-participating stock pays a lower amount to its holders and the participating stock does not. A company that issues participating preferred stock will pay out a fixed dollar per share for its shareholders, while common stockholders receive a fixed dollar each year.
There is a major difference between a participating preferred stock and a common stock. The first will be treated differently by the company. A participant preferred stock is entitled to the first payment. The non-participating version does not have any rights and obligations. The non-participating preferredstock holder will not be eligible to share in liquidation proceeds.
FAQ
How are Share Prices Set?
Investors decide the share price. They are looking to return their investment. They want to make money from the company. They then buy shares at a specified price. Investors will earn more if the share prices rise. If the share price falls, then the investor loses money.
An investor's main objective is to make as many dollars as possible. This is why they invest into companies. It helps them to earn lots of money.
What is security at the stock market and what does it mean?
Security is an asset which generates income for its owners. Most security comes in the form of shares in companies.
Different types of securities can be issued by a company, including bonds, preferred stock, and common stock.
The earnings per share (EPS), as well as the dividends that the company pays, determine the share's value.
When you buy a share, you own part of the business and have a claim on future profits. If the company pays you a dividend, it will pay you money.
You can always sell your shares.
What is the distinction between marketable and not-marketable securities
The principal differences are that nonmarketable securities have lower liquidity, lower trading volume, and higher transaction cost. Marketable securities, on the other hand, are traded on exchanges and therefore have greater liquidity and trading volume. Because they trade 24/7, they offer better price discovery and liquidity. But, this is not the only exception. For instance, mutual funds may not be traded on public markets because they are only accessible to institutional investors.
Non-marketable securities tend to be riskier than marketable ones. They are generally lower yielding and require higher initial capital deposits. Marketable securities can be more secure and simpler to deal with than those that are not marketable.
For example, a bond issued in large numbers is more likely to be repaid than a bond issued in small quantities. This is because the former may have a strong balance sheet, while the latter might not.
Investment companies prefer to hold marketable securities because they can earn higher portfolio returns.
Are bonds tradeable?
Yes they are. You can trade bonds on exchanges like shares. They have been for many years now.
They are different in that you can't buy bonds directly from the issuer. They must be purchased through a broker.
It is much easier to buy bonds because there are no intermediaries. This means you need to find someone willing and able to buy your bonds.
There are several types of bonds. Some bonds pay interest at regular intervals and others do not.
Some pay interest every quarter, while some pay it annually. These differences allow bonds to be easily compared.
Bonds are very useful when investing money. For example, if you invest PS10,000 in a savings account, you would earn 0.75% interest per year. This amount would yield 12.5% annually if it were invested in a 10-year bond.
If you were to put all of these investments into a portfolio, then the total return over ten years would be higher using the bond investment.
What's the role of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)?
The SEC regulates securities exchanges, broker-dealers, investment companies, and other entities involved in the distribution of securities. It also enforces federal securities law.
What is the difference in the stock and securities markets?
The securities market refers to the entire set of companies listed on an exchange for trading shares. This includes stocks, bonds, options, futures contracts, and other financial instruments. Stock markets can be divided into two groups: primary or secondary. The NYSE (New York Stock Exchange), and NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) are examples of large stock markets. Secondary stock markets are smaller exchanges where investors trade privately. These include OTC Bulletin Board Over-the-Counter and Pink Sheets as well as the Nasdaq smallCap Market.
Stock markets are important because it allows people to buy and sell shares in businesses. The value of shares depends on their price. When a company goes public, it issues new shares to the general public. Dividends are paid to investors who buy these shares. Dividends are payments made by a corporation to shareholders.
Stock markets are not only a place to buy and sell, but also serve as a tool of corporate governance. Boards of directors, elected by shareholders, oversee the management. They ensure managers adhere to ethical business practices. In the event that a board fails to carry out this function, government may intervene and replace the board.
Statistics
- The S&P 500 has grown about 10.5% per year since its establishment in the 1920s. (investopedia.com)
- US resident who opens a new IBKR Pro individual or joint account receives a 0.25% rate reduction on margin loans. (nerdwallet.com)
- Our focus on Main Street investors reflects the fact that American households own $38 trillion worth of equities, more than 59 percent of the U.S. equity market either directly or indirectly through mutual funds, retirement accounts, and other investments. (sec.gov)
- Individuals with very limited financial experience are either terrified by horror stories of average investors losing 50% of their portfolio value or are beguiled by "hot tips" that bear the promise of huge rewards but seldom pay off. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How can I invest my money in bonds?
An investment fund is called a bond. They pay you back at regular intervals, despite the low interest rates. You can earn money over time with these interest rates.
There are several ways to invest in bonds:
-
Directly buy individual bonds
-
Buy shares in a bond fund
-
Investing through a broker or bank
-
Investing through a financial institution
-
Investing in a pension.
-
Directly invest through a stockbroker
-
Investing through a Mutual Fund
-
Investing through a unit trust.
-
Investing via a life policy
-
Investing through a private equity fund.
-
Investing through an index-linked fund.
-
Investing through a hedge fund.